How do you Backtest a Trading Strategy?
Trading
Ever had a brilliant trading idea, jumped in with real money, and watched it fall apart within hours? Maybe you read about a strategy online, tried it immediately, and lost more than you expected.
You're not alone. Most beginner traders make this exact mistake.
There's a way to test your trading ideas before risking real money. It's called backtesting, and it's one of the most valuable skills you can learn as a trader. Think of it as a "practice run" using historical data to see if your strategy actually works—without losing a single dollar in the process.
In this article, we'll break down exactly what backtesting is, why it matters so much, and how you can start doing it yourself—even if you've never done it before. By the end, you'll know how to test your trading ideas before putting real money on the line.
What is Backtesting?
Backtesting is testing a trading strategy using historical price data to see how it would have performed in the past.
Imagine you invented a new recipe. Would you serve it at a dinner party without tasting it first? Probably not. You'd test it, adjust the seasoning, maybe try it a few times until you're confident it works. Backtesting is the same idea for trading. You're "tasting" your strategy on past market data before serving it up with real money.
Here's a simple example:
Let's say you have a strategy: "Buy Bitcoin when the price drops 10% in one week, and sell when it rises 5% from your entry." Backtesting means going back through historical Bitcoin charts and checking: If I had followed this rule over the past year, would I have made money or lost money?
You'd look at every time Bitcoin dropped 10% in a week, note what happened next, and tally up your wins and losses.
The results tell you whether your idea has potential—or whether it's a recipe for disaster.
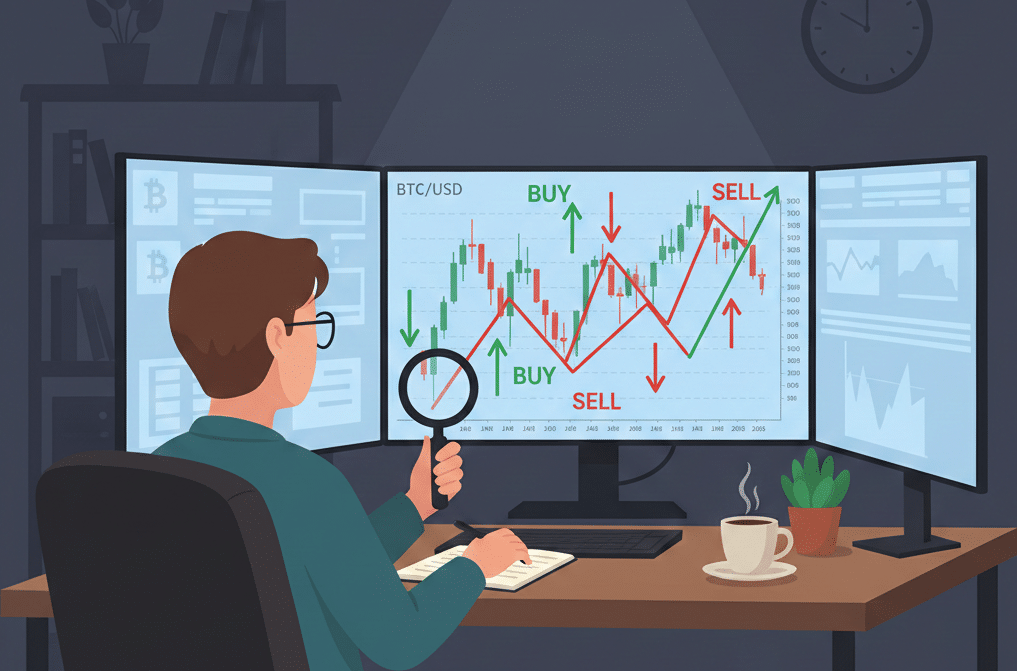
Why Backtesting Matters (Especially for Beginners)
You might be thinking: "Can't I just paper trade instead?" Paper trading (using fake money in real-time) is valuable, but it has one big limitation: it's slow. You have to wait for the market to move.
Backtesting lets you simulate months or even years of trading in just a few hours. Here's why that matters:
You find out fast if your idea works. Instead of spending six months discovering your strategy loses money, you can find out in an afternoon. That saves you time, money, and frustration.
You remove emotion from the equation. When you're backtesting, you're not stressed about real money. You can think clearly and evaluate results objectively. In live trading, fear and greed often cloud judgment.
You build confidence. If you've tested a strategy on hundreds of trades and seen positive results, you'll trust it more when things get tough in live markets. That confidence helps you stick to your plan instead of panic-selling.
You can compare strategies. Have two trading ideas? Backtest both and see which one performs better. Data beats guessing.
💡 Pro Tip: A strategy that looks amazing in your head might perform terribly in reality. Backtesting is how you separate good ideas from bad ones before they cost you money.
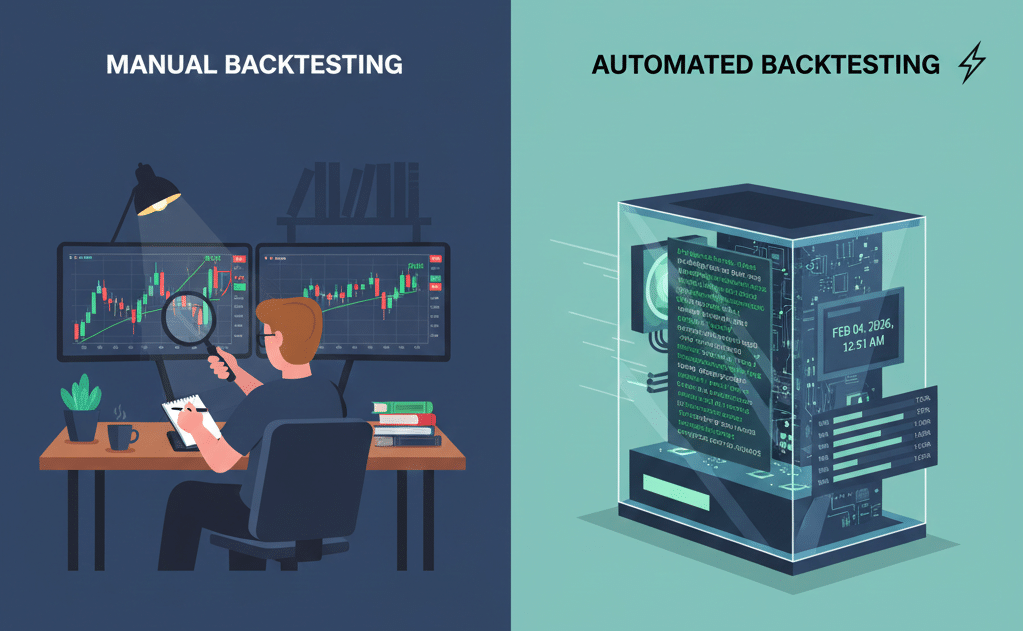
The Two Ways to Backtest
There are two main approaches to backtesting: manual and automated. Let's look at both.
Manual Backtesting
This is the simplest approach and requires no coding or special software. You scroll through historical charts, identify where your strategy would have triggered trades, and record the results in a spreadsheet.
How manual backtesting works:
- Open a charting platform (like TradingView—it's free)
- Pick a coin and timeframe (e.g., Bitcoin on the 4-hour chart)
- Scroll back in time—maybe 6 months or a year
- Look for moments when your strategy rules are met
- Note the entry price, exit price, and whether the trade won or lost
- Move forward and repeat
- Tally your results at the end
Manual backtesting is slower, but it has a huge advantage: you actually learn the market. By going through charts trade-by-trade, you start recognizing patterns and understanding how price moves. Many professional traders swear by manual testing for this reason.
Automated Backtesting
If you have coding skills (or use platforms that offer it), you can automate the process. You program your strategy rules, feed in historical data, and the software calculates results instantly. Platforms like TradingView (with Pine Script) or dedicated backtesting tools let you do this. Automated testing is faster and can process thousands of trades in seconds.
However, automated backtesting has risks. It's easy to "overfit" your strategy—tweaking it until it looks perfect on past data but fails in live markets. We'll talk more about that later. For beginners, manual backtesting is usually better. It's simpler, and the hands-on process teaches you more about how markets behave.
Step-by-Step: How to Backtest Your Trading Strategy
Ready to try it yourself? Here's a simple process you can follow today.
Step 1: Define Your Strategy Clearly
Before you test anything, you need clear, specific rules. Vague ideas like "buy when it looks cheap" won't work. Your rules need to be objective—meaning anyone following them would make the same decisions.
Good strategy rules include:
- Entry conditions: Exactly when do you buy? (e.g., "When RSI drops below 30 AND price is above the 200-day moving average")
- Exit conditions: Exactly when do you sell? (e.g., "When price rises 8% from entry OR drops 3% from entry")
- Position size: How much do you risk per trade?
Write these rules down. Be specific.
Step 2: Choose Your Market and Timeframe
Decide what you're testing:
- Which coin? (Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.)
- Which timeframe? (1-hour, 4-hour, daily charts?)
- How far back will you test? (3 months? 1 year? 5 years?)
A good rule of thumb: test across at least 50-100 trades to get meaningful results. If your strategy only triggers 5 trades per year, you'll need more historical data.
Step 3: Gather Historical Data
Most charting platforms provide free historical data. TradingView, for example, lets you scroll back years on most crypto pairs.
For backtesting, you want clean, accurate data. Stick to reputable platforms.
Step 4: Test the Strategy
Now comes the actual work. Go through the charts and mark every trade your strategy would have taken. For each trade, record:
- Entry date and price
- Exit date and price
- Profit or loss (in percentage or dollar amount)
- Any notes about what happened
Be honest. Don't skip trades that would have been losers. The whole point is to get an accurate picture.
Step 5: Analyze Your Results
Once you've tested enough trades, calculate key metrics:
- Win rate: What percentage of trades were profitable?
- Average win vs. average loss: How much do you make when you win compared to how much you lose when you're wrong?
- Total return: If you started with $1,000, where would you be now?
- Maximum drawdown: What was the biggest losing streak? How much would your account have dropped at its worst point?
These numbers tell you whether your strategy has a real edge—or whether it's just random.
Example spreadsheet showing backtest results with columns for date, entry price, exit price, profit/loss, and running total. Image Source: Tradeinformed
Key Metrics to Track (And What They Mean)
When analyzing your backtest, focus on these numbers:
Win Rate
This is the percentage of trades that were profitable. A 60% win rate means 6 out of every 10 trades made money.
But here's the catch: win rate alone doesn't tell the whole story. A strategy can have a 40% win rate and still be profitable if the average win is much larger than the average loss.
Risk-Reward Ratio
This compares how much you stand to gain versus how much you risk. If your average winning trade makes $200 and your average losing trade costs $100, your risk-reward ratio is 2:1.
Higher is generally better. A 2:1 ratio means you only need to win 1 out of 3 trades to break even.
Maximum Drawdown
This measures the worst peak-to-trough decline during your backtest. If your account went from $10,000 to $7,000 at its lowest point, your maximum drawdown was 30%.
Why does this matter? Because drawdowns are painful. A strategy might be profitable overall but have such brutal losing streaks that you'd abandon it before it recovers. Know what you're signing up for.
Expectancy
This is your average profit per trade when you factor in both wins and losses. Positive expectancy means the strategy makes money over time. Negative expectancy means it loses money.
Formula: (Win Rate × Average Win) – (Loss Rate × Average Loss)
If expectancy is positive, you have something worth pursuing.
⚠️ Common Mistake: Getting excited about a high win rate without checking the risk-reward ratio. A strategy that wins 80% of the time but loses big on the other 20% can still destroy your account.
Common Backtesting Mistakes to Avoid
Backtesting is powerful, but it's easy to do it wrong. Watch out for these traps:
Overfitting (Curve Fitting)
This happens when you tweak your strategy so much that it perfectly matches past data—but fails in the future. It's like memorizing the answers to a test instead of understanding the material. When the questions change, you fail.
How to avoid it: Keep your rules simple. If you need 15 conditions for a trade to trigger, you're probably overfitting. Also, test on "out-of-sample" data—data you didn't use while developing the strategy.
Survivorship Bias
If you only backtest coins that exist today, you're ignoring the ones that failed. This makes your results look better than reality.
How to avoid it: Be aware of this limitation. Consider testing on major coins (like Bitcoin and Ethereum) that have long histories.
Ignoring Trading Costs
Every trade has costs: exchange fees, spread (the difference between buy and sell prices), and sometimes slippage (getting a worse price than expected). These add up fast.
How to avoid it: Factor in realistic fees. If your exchange charges 0.1% per trade, include that in your calculations.
Cherry-Picking Results
It's tempting to skip losing trades or only count the good ones. Don't. That defeats the entire purpose.
How to avoid it: Record every single trade, win or lose. Be brutally honest with yourself.
Testing Too Few Trades
Five trades isn't enough data. Neither is twenty. You need enough samples to separate skill from luck.
How to avoid it: Aim for at least 50-100 trades before drawing conclusions.
What Happens After Backtesting?
Your backtest looked promising. Now what?
Forward Testing (Paper Trading)
Before risking real money, test your strategy in real-time with fake money. This is called paper trading or forward testing. It reveals problems that backtesting can't catch—like how you react emotionally or whether you can actually execute the trades as planned.
Spend 2-4 weeks paper trading. If the results still look good, you're ready for the next step.
Start Small with Real Money
When you finally go live, start with a small amount—money you can afford to lose completely. Your first live trades are about validating your strategy, not getting rich.
Increase your position size only after you've proven the strategy works in real market conditions.
Quick Recap
Here's what we covered:
- Backtesting is testing your strategy on historical data to see how it would have performed
- Manual backtesting is best for beginners—it's simple and teaches you a lot about markets
- Clear rules are essential—your strategy needs specific, objective entry and exit conditions
- Key metrics to track include win rate, risk-reward ratio, maximum drawdown, and expectancy
- Avoid common mistakes like overfitting, ignoring fees, and testing too few trades
- Paper trade your strategy after backtesting before risking real money
What Should You Do Next?
Backtesting might sound like extra work, but it's the kind of work that saves you money in the long run. The traders who skip this step often pay for it with painful losses.
Your Next Steps:
- Today: Pick one simple strategy you've been curious about. Write down the exact rules—entry, exit, position size. Be specific enough that a stranger could follow them.
- This Week: Open TradingView (it's free), pick Bitcoin or Ethereum, and manually backtest your strategy on the past 3-6 months of data. Record at least 30 trades in a spreadsheet. Calculate your win rate and risk-reward ratio.
- Ongoing: Join the Fat Pig Signals Telegram community. We share strategies, discuss what's working, and help each other improve. Learning to backtest is easier when you're doing it alongside other traders who can answer questions and share insights.
Remember: every professional trader backtests their ideas. It's not optional—it's how you separate strategies that work from strategies that just sound good. The time you invest in backtesting pays off in saved losses and better decisions.
You don't need to be a coding genius or a math wizard. You just need patience, honesty, and a willingness to learn. Start simple, stay consistent, and trust the process.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Cryptocurrency trading involves substantial risk of loss. Always do your own research and consider consulting with a financial advisor before making investment decisions.



